AI바라기의 인공지능
LLM : 논문리뷰 : RedStar: Does Scaling Long-CoT Data Unlock Better Slow-Reasoning Systems? 본문
LLM : 논문리뷰 : RedStar: Does Scaling Long-CoT Data Unlock Better Slow-Reasoning Systems?
AI바라기 2025. 1. 27. 14:36RedStar: Does Scaling Long-CoT Data Unlock Better Slow-Reasoning Systems? 논문 정리 노트
Purpose of the Paper (논문의 목적)
- Long-CoT 데이터 스케일링의 잠재력 탐구: 기존 연구들은 주로 Long-CoT 데이터의 양적, 질적 스케일링 효과에 대한 심층적인 분석이 부족했음. 본 논문은 Long-CoT 데이터를 대규모로 확장했을 때, 특히 복잡한 추론 능력이 필요한 시스템에 미치는 영향을 체계적으로 분석하고자 함.
- Slow-Reasoning 시스템 발전을 위한 핵심 요소 규명: 단순히 데이터 양을 늘리는 것을 넘어, Long-CoT 학습에 있어 모델 크기, 특화 (specialization), 효과적인 학습 전략 등 중요한 구성 요소들을 밝혀내고자 함.
- 다양한 도메인 및 모델에 대한 Long-CoT 효과 검증: 수학 문제 해결뿐만 아니라 multimodal tasks와 같은 다양한 영역에서 Long-CoT 방법론의 범용성과 효과를 입증하고자 함. 기존 연구들이 주로 특정 task에 집중했던 것에 비해, 본 연구는 더욱 폭넓은 시각에서 Long-CoT의 잠재력을 평가함.
- 새로운 Slow-Thinking 모델 RedStar 제시: Long-CoT 데이터 스케일링과 RL-scale training을 통해 고성능 Slow-Thinking 모델인 RedStar를 개발하고, 다양한 벤치마크에서 성능을 검증하여 Long-CoT 방법론의 우수성을 실증적으로 보여주고자 함.
Key Contributions (핵심 기여)
- Long-CoT 데이터 스케일링 효과 입증: 실험을 통해 Long-CoT 데이터 규모가 커질수록 모델의 추론 능력이 지속적으로 향상됨을 보여줌. 특히 복잡한 문제 (MATH-hard, Olympiad-bench)에서 데이터 스케일링 효과가 더욱 두드러지게 나타남.
- Long-CoT 학습의 Sample Efficiency 강조: 적은 양의 데이터 (1.3k prompts)만으로도 Long-COT fine-tuning을 통해 추론 성능을 크게 향상시킬 수 있음을 밝힘. 이는 Long-CoT 방법론의 데이터 효율성을 강조하며, limited data 환경에서도 효과적인 추론 시스템 구축 가능성을 시사함.
- 모델 크기 및 특화의 중요성: 더 큰 모델 (14B, 32B)과 specialized models (Math Pretraing)이 Long-COT 학습에서 더 나은 성능을 보임을 입증. 모델의 capacity와 task-specific tuning이 Long-COT 효과를 극대화하는 데 중요한 역할을 함을 밝힘.
- Positive transfer across tasks and language: Long-COT 학습이 수학 task뿐만 아니라 다른 도메인 및 언어에도 긍정적인 영향을 미치는 것을 확인. Long-COT 방법론의 versatility와 generalization 능력을 보여줌.
- RL-scale training의 효과: Offline RL (DPO) 및 online RL (PPO) 알고리즘을 Long-COT 학습에 적용하여 성능 향상을 이끌어냄. RL-scale training이 Slow-Thinking 시스템 발전을 위한 promising direction임을 제시.
- Multimodal tasks에서의 Long-COT 효과 입증: Multimodal LLM (MLLM)에 Long-COT 방법론을 적용하여 geometric question-answering task에서 substantial improvements를 달성. Long-COT의 multimodal context에서의 versatility를 보여줌.
- 새로운 Slow-Thinking 모델 RedStar 공개: RedStar 모델과 학습 데이터, 코드를 공개하여 Slow-Reasoning 연구 발전에 기여.
Novelty (새로움)
- Long-CoT 데이터 스케일링에 대한 체계적인 탐구: 기존 연구들이 Long-CoT 자체의 효과에 집중했던 반면, 본 연구는 Long-CoT 데이터의 스케일링 효과를 집중적으로 분석하고, 다양한 데이터 크기 및 모델 규모에 따른 성능 변화를 실증적으로 검증함.
- RL-scale training과 Long-COT 결합: Reinforcement learning을 Long-COT 학습에 통합하여 모델 성능을 더욱 향상시키는 새로운 접근 방식을 제시. 특히 DPO와 PPO 알고리즘을 Long-COT fine-tuning에 효과적으로 적용한 점이 novel함.
- Multimodal Long-CoT 연구: Multimodal tasks에 Long-COT 방법론을 확장 적용하고 성공적인 결과를 도출함. 텍스트 기반 추론에 집중되었던 Long-COT 연구를 multimodal 영역으로 넓혔다는 점에서 novelty를 가짐.
- Sample Efficiency에 대한 강조: Long-COT 학습이 소량의 데이터로도 효과적임을 강조하며, high-quality Long-COT 데이터 구축의 중요성을 강조함. 이는 대규모 데이터에 의존하는 기존 LLM 연구와 차별화되는 novelty임.
Experimental Highlights (실험 주요 결과)
- Data Scaling Experiments:
- Long-COT 데이터 규모 증가에 따라 모델 성능 지속적으로 향상 (Table 1).
- 작은 모델 (7B-Instruct)은 larger datasets에서 substantial benefits, 큰 모델 (14B-Instruct)은 smaller datasets에서도 notable improvements.
- 7B-Math-Instruct 모델은 4k Long-COT 예시에서 36.8% -> 41.0% 성능 향상, 1000k 예시에서 45.4%까지 향상.
- 14B-Instruct 모델도 data scaling에 따라 성능 향상, 평균 점수 35.8% -> 44.3%.
- Sample efficiency 비교: 0-4k 예시에서 작은 7B-Instruct 모델은 minimal improvement, 큰 14B-Instruct, 7B-Math-Instruct 모델은 significant improvement (8.5%, 4.2%).
- Difficulty-Level Experiments:
- Hard-level prompts에서 Long-COT fine-tuning 효과 가장 큼 (Table 2).
- High difficulty prompts에서 14B-Instruct 모델은 69.2% -> 49.8% (Olympiad) -> 42.7% (College) -> 36.7% (High School) -> 23.3% (AIME24) -> 44.3% (AVG) 성능 향상.
- RL-scale training Experiments:
- DPO, PPO 모두 RL fine-tuning을 통해 성능 향상 (Table 3).
- DPO, PPO 모두 평균 점수 47.2% 달성, REINFORCE++는 45.9%.
- DPO는 college_math (46.1%), high_school_league (40.0%)에서 뛰어난 성능, PPO는 math-hard (69.9%), high_school_league (44.2%)에서 뛰어난 성능.
- Multimodal Experiments (RedStar-Geo-8B):
- RedStar-Geo-8B 모델은 GeoQA, MathVista-GEO, Geometry3K 벤치마크에서 state-of-the-the-art 모델 (GPT-4V, GPT-4o) 및 다른 open-source MLLM 모델 (QvQ-72B-Preview)과 competitive performance 달성 (Table 7).
- 특히 적은 양의 Long-COT instruction (3.7K)으로 large instruction datasets (Geo-Intern2VL-8B: 170K, Math-LLaVA-13B: 834K)로 학습된 모델들과 comparable performance.
- General Capability Benchmarks (Table 5):
- RedStar-code-math 모델은 STEM, Reasoning, Factuality, LongGen (Hellobench), SedarEval 벤치마크에서 Qwen-QwQ-32B보다 높은 평균 점수 (68.8% vs 62.8%) 기록.
- STEM task에서 Qwen2.5-32B-Instruct와 유사한 성능 (79.2% vs 80.1%).
- Reasoning task에서 Qwen-QwQ-32B보다 약간 높은 성능 (73.1% vs 73.0%).
- Factuality task에서 가장 높은 점수 (36.0%).
- Long Generation task에서 Qwen2.5-32B-Instruct와 유사한 성능 (87.1% vs 88.0%).
- OOD Test (Chinese Graduate Entrance Mathematics Test datasets - Table 6):
- RedStar-code-math 모델은 closed-source API (DeepSeek-R1, Kimi-Math), open-source 모델 (QwQ)과 comparable performance.
- 영어 datasets로 학습했음에도 불구하고 Chinese OOD-tests에서 우수한 language transfer capabilities 보여줌.
Limitations (제한점)
- CommonSense Performance: RedStar는 CommonSense tasks에서 Qwen2.5-32B-Instruct보다 낮은 성능을 보임 (Table 5). Common sense 능력을 향상시키기 위한 추가적인 연구 필요.
- SedarEval Score: SedarEval 벤치마크에서 Qwen2.5-32B-Instruct보다 약간 낮은 점수를 기록 (Table 5). SedarEval 평가에서 성능 격차를 줄이기 위한 추가적인 training optimizations 필요.
- Step-by-Step Verification Failure: Step-by-step verification 방법이 Long-COT 성능 향상에 significant improvement를 가져오지 못함 (Appendix A, Table 8). 더 robust하고 scalable한 oversight mechanism 개발 필요.
- Long Text Generation (Over 4000 words): RedStar를 포함한 모델들이 매우 긴 텍스트 (4000 단어 이상) 생성 시 repetition 및 quality degradation 문제 발생. long-context reasoning capabilities 개선 필요.
- General Alignment Tasks에서의 성능 감소 (Appendix C.7): 작은 모델 (7B)의 경우 Long-COT 데이터 규모가 커질수록 general alignment tasks (Hellobench, Sedareval)에서 성능이 감소하는 현상 발생. catastrophic forgetting 문제 완화 필요.
Future Work (향후 연구 방향)
- Instruction-tuned 모델 기반 High-Quality Long-COT 데이터셋 합성: Instruct 모델만을 사용하여 high-quality Long-COT 데이터셋을 합성하는 방법 연구. Long-COT 학습 접근성 향상 및 확장성, 자동화된 데이터 생성 가능성 증대 기대.
- Long-COT를 더 복잡한 벤치마크로 확장: Long-COT 방법론의 generalization potential을 further evaluate하기 위해 더 복잡한 벤치마크 (e.g., more diverse multimodal tasks, real-world reasoning scenarios)로 확장 연구 진행.
- Long-COT 데이터 품질 및 다양성 향상 연구: Multi-source data synthesis, prompt augmentation, active learning 등 다양한 방법을 통해 Long-COT 데이터 품질과 다양성을 더욱 향상시키는 연구 필요.
- RL-scale training 최적화: DPO, PPO 등 RL 알고리즘의 hyperparameter tuning, reward function design 등을 최적화하여 Long-COT 기반 Slow-Thinking 시스템 성능 극대화 연구.
- Long-COT 기반 Multimodal Reasoning 모델 발전: RedStar-Geo 모델을 기반으로 multimodal Long-COT 방법론을 더욱 발전시키고, 다양한 multimodal tasks에서의 성능 향상 연구. 특히 geometric reasoning task 외 다른 multimodal reasoning challenges에 대한 연구 확장.
Abstract
Scaling이 reasoning을 변화시킬 수 있을까요? 본 연구에서는 1000k 샘플로 Long Chain-of-Thought (Long-CoT) 데이터의 scaling의 미개척된 잠재력을 탐구하여 slow-thinking model인 RedStar 개발을 개척합니다. 다양한 LLMs와 다양한 크기를 사용한 광범위한 실험을 통해 Long-CoT training을 위한 specialization과 scale의 요소를 밝혀냅니다. 놀랍게도, 더 작은 models조차 제한된 데이터로 상당한 performance 향상을 보여 Long-CoT의 sample efficiency와 learning 과정에서 sample difficulty의 중요한 역할을 드러냅니다. 우리의 연구 결과는 Long-CoT reasoning이 단지 몇 천 개의 예시만으로도 효과적으로 촉발될 수 있으며, 더 큰 models는 비할 데 없는 improvements를 달성한다는 것을 보여줍니다. 우리는 또한 slow-thinking systems 발전을 위한 유망한 방향으로 reinforcement learning (RL)-scale training을 소개합니다. RedStar는 여러 domains에서 빛을 발합니다: MATH-Hard benchmark에서 RedStar-code-math는 performance를 66.2%에서 81.6%로 향상시키고, USA Math Olympiad (AIME)에서는 단 21k mixed-code-math datasets만 사용하여 문제의 46.7%를 해결합니다. GeoQA 및 MathVista-GEO와 같은 multimodal tasks에서 RedStar-Geo는 최소한의 Long-CoT 데이터로 경쟁력 있는 results를 달성하여 QvQ-Preview와 같은 다른 slow-thinking systems보다 뛰어난 성능을 보입니다. QwQ와 비교했을 때, RedStar는 reasoning과 generalizability 사이에서 완벽한 균형을 이룹니다. 우리의 연구는 세심한 tuning을 통해 Long-CoT의 scaling이 제한된 dataset으로도 특별한 reasoning capabilities를 발휘하고 다양한 challenges에서 slow-thinking models에 대한 새로운 standard를 설정할 수 있음을 강조합니다.
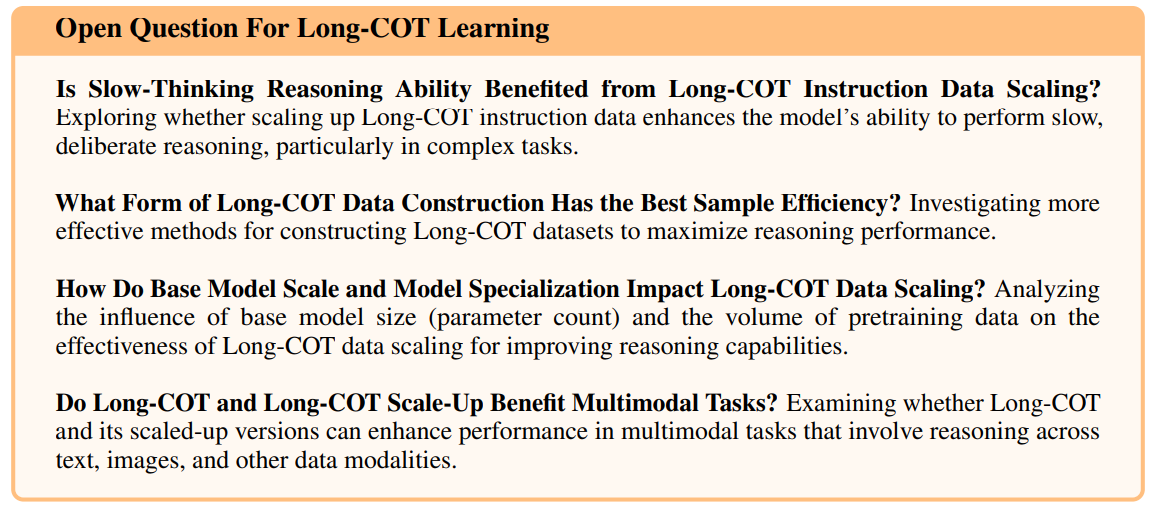
Is Slow-Thinking Reasoning Ability Benefited from Long-COT Instruction Data Scaling?
Long-COT Instruction Data Scaling으로부터 Slow-Thinking Reasoning 능력은 이점을 얻을 수 있을까요?
Exploring whether scaling up Long-COT instruction data enhances the model’s ability to perform slow, deliberate reasoning, particularly in complex tasks.
특히 복잡한 tasks에서 Long-COT instruction data를 scaling up하는 것이 slow하고 신중한 reasoning을 수행하는 model의 능력을 향상시키는지 탐구합니다.
What Form of Long-COT Data Construction Has the Best Sample Efficiency?
어떤 형태의 Long-COT Data Construction이 가장 Sample Efficiency가 좋을까요?
Investigating more effective methods for constructing Long-COT datasets to maximize reasoning performance.
Reasoning performance를 최대화하기 위해 Long-COT datasets를 구축하는 더 효과적인 방법들을 조사합니다.
How Do Base Model Scale and Model Specialization Impact Long-COT Data Scaling?
Base Model Scale과 Model Specialization은 Long-COT Data Scaling에 어떤 영향을 미칠까요?
Analyzing the influence of base model size (parameter count) and the volume of pretraining data on the effectiveness of Long-COT data scaling for improving reasoning capabilities.
Reasoning capabilities 향상을 위한 Long-COT data scaling의 효과에 대한 base model 크기 (parameter 수) 및 pretraining data의 양의 영향을 분석합니다.
Do Long-COT and Long-COT Scale-Up Benefit Multimodal Tasks?
Long-COT과 Long-COT Scale-Up은 Multimodal Tasks에 이점을 줄까요?
Examining whether Long-COT and its scaled-up versions can enhance performance in multimodal tasks that involve reasoning across text, images, and other data modalities.
Long-COT과 그것의 scaled-up 버전이 text, images 및 기타 data modalities에 걸친 reasoning을 포함하는 multimodal tasks에서 performance를 향상시킬 수 있는지 조사합니다.
1 Introduction
LLM-driven Slow-thinking reasoning systems은 o12 및 variants—DeepSeek-R13, k0-math4, Macro-o1 [1], and QwQ5—와 같은 models로 대표되며, 복잡한 reasoning challenges를 해결하기 위한 새로운 길을 열었습니다. 이러한 발전의 핵심에는 빠르고 피상적인 responses보다 체계적이고 단계별 reasoning을 우선시하는 long chain-of-thought (Long-COT) paradigm이 있습니다. 이 approach는 구조화되고 논리적인 steps이 정확한 conclusions에 필수적인 mathematical problem-solving과 같은 tasks에서 특히 효과적인 것으로 입증되었습니다. Long-COT의 success는 복잡한 problems을 더 작고 관리하기 쉬운 sub-tasks로 분해하는 능력에서 비롯되며, 이는 인간의 cognitive processes를 반영하고 더 깊고 분석적인 reasoning을 촉진합니다.
Recent advancements in slow-thinking reasoning systems은 tree-search-based 및 distillation-based methods로 분류할 수 있습니다. Tree-search approaches는 다양한 reasoning paths [1–3]를 탐색하기 위해 data synthesis 및 search strategies를 사용하고, distillation methods는 high-quality reasoning chains [4–7]로 fine-tuning하여 performance를 refining하는 데 중점을 둡니다. 두 approaches 모두 models의 step-by-step reasoning capabilities를 향상시키기 위해 synthetic Long-COT data를 활용합니다. 그러나 그들의 contributions에도 불구하고 Long-COT datasets의 scalability—volume과 quality 측면 모두에서—는 thoroughly investigated되지 않았습니다. 또한 multi-source data synthesis, model capacity, effective training strategies 및 multimodal integration과 같은 key factors는 underexplored 상태로 남아 있습니다. 이러한 limitations은 다양하고 복잡한 tasks에서 reasoning performance를 optimizing하기 위한 Long-COT의 broader adoption을 hinder합니다.
In this paper에서는 Question-Box 1의 data scaling up 관점에서 Long-COT의 potential을 investigate합니다. 우리는 general data로부터 large volume의 Long-COT를 constructing하는 데 scaling effect가 존재하는지, 특히 Long-COT scaling에 대한 different model bases 및 model parameter scales의 influence에 대해 answer하려고 시도합니다. 우리는 moderate difficulty level에서 properly synthesized된 경우, even small datasets도 reasoning capabilities에서 significant improvements로 이어질 수 있음을 demonstrate합니다. Specifically, 우리는 1.3k prompts와 4k prompt-response pairs로 구성된 dataset을 curate하며, 이는 supervised manner로 reasoning models를 fine-tune하는 데 사용됩니다. The results는 Long-COT fine-tuning이 a range of reasoning tasks에서 substantial performance improvements를 산출한다는 것을 indicate합니다.
We first explore varying data sizes 및 model configurations이 Long-COT scaling tuning에 미치는 impact를 explore합니다. Our findings는 larger datasets가 특히 complex reasoning tasks에서 performance에서 significant gains로 이어진다는 것을 보여줍니다. 7B-Instruct와 같은 smaller models는 larger datasets로부터 substantially benefit을 얻는 반면, 14B-Instruct와 같은 larger models는 even smaller datasets에서도 notable improvements를 보여줍니다. This underscores reasoning performance를 optimizing하는 데 있어 data scaling과 model capacity 모두의 importance를 강조하며, tailored data sizes가 model’s capabilities에 따라 training efficiency를 enhance할 수 있음을 suggesting합니다.
To further refine Long-COT의 effectiveness를 높이기 위해 reinforcement learning (RL) strategies를 incorporate합니다. RL-based training은 models가 feedback을 통해 그들의 reasoning을 refine할 수 있도록 하여, iterative problem-solving 및 fine-tuned decision-making을 handle하는 그들의 ability를 improving합니다. Our experiments는 RL techniques가 enhanced reasoning quality로 이어져 Long-COT’s performance를 further optimizing한다는 것을 demonstrate합니다.
Data Scaling experiments에서 base model characteristics 및 data scale에 대한 우리의 observations를 바탕으로, 우리는 4k-scale Long-COT instruction set을 constructed하고 corresponding Qwen-32B-Instruct에서 Slow-Thinking model을 developed했습니다. The results는 significant performance improvements를 보여주며, 32B model은 smaller models에 비해 better reasoning consistency와 complex tasks의 superior handling을 exhibiting하여 intricate reasoning problems에 대한 Long-COT methods의 scalability를 confirming합니다.
Moreover, 우리는 Long-COT의 application을 multimodal large language models (MLLMs)로 extend하여 textual 및 visual data를 combine하는 tasks를 addressing합니다. Geometric question-answering tasks에 step-by-step reasoning을 integrating함으로써 substantial improvements를 achieve하여 textual 및 multimodal contexts 모두에서 Long-COT의 versatility를 demonstrating합니다.
Our findings는 다양한 domains 및 modalities에서 reasoning models를 advancing하기 위한 Long-COT의 transformative potential을 highlight합니다. Mathematical problem-solving에 applied되든, multimodal challenges에 applied되든, Long-COT tuning은 reasoning capabilities를 enhancing하기 위한 essential tool임이 proves됩니다. Our final model인 RedStar는 leading reasoning model로 emerges하여 Long-COT methodologies의 broad impact를 demonstrating합니다.
정리노트: Long-COT 데이터 스케일링 연구 (Introduction 섹션)
핵심 질문: Long Chain-of-Thought (Long-COT) 데이터 스케일링이 복잡한 Reasoning 능력 향상에 효과적인가?
연구 배경 및 문제점:
- Long-COT의 중요성: LLM 기반 Slow-thinking reasoning 모델 (o12, DeepSeek-R, QwQ 등)은 복잡한 문제 해결에 효과적인 접근 방식인 Long-COT 패러다임을 활용. 단계별 논리적 추론을 통해 수학 문제 해결 등에서 강점 입증.
- 기존 연구의 한계: Tree-search, Distillation 기반 Long-COT 연구는 존재하나, Long-COT 데이터셋의 스케일링 (양과 질) 에 대한 체계적인 연구 부족. 데이터 합성, 모델 크기, 훈련 전략, Multimodal 통합 등 핵심 요소 미탐구. → 다양한 Task에서 Long-COT 최적화 및 확장에 제약 발생.
본 연구의 차별점 및 핵심 기여:
- 데이터 스케일링 관점: Long-COT의 잠재력을 데이터 스케일링 측면에서 집중적으로 탐구. "일반 데이터로부터 대규모 Long-COT 데이터 구축 시 스케일링 효과가 있는가?" 라는 핵심 질문 제시.
- 모델 규모 및 특성 영향 분석: Long-COT 스케일링 효과에 대한 모델 Base 및 Parameter Scale 의 영향 분석.
- 샘플 효율성 발견: 적절한 난이도로 합성된 소규모 데이터셋 만으로도 Reasoning 능력의 Significant 향상 가능성 입증 (1.3k prompt, 4k prompt-response pairs 데이터셋 활용). → Long-COT의 Sample Efficiency 강조.
- 데이터 크기 및 모델 설정 실험: 다양한 데이터 크기와 모델 (7B, 14B) 설정을 통해 Long-COT 스케일링 효과 분석. 대규모 데이터셋이 복잡한 Reasoning Task에서 성능 향상에 크게 기여함을 확인. 모델 크기에 따라 최적 데이터 규모가 다를 수 있음을 시사.
- RL 활용: Reinforcement Learning (RL) 기반 훈련을 통해 Long-COT 효과 극대화. 피드백 기반 Reasoning 개선 및 반복적 문제 해결 능력 향상.
- RedStar 모델 개발 및 성능 입증: 4k 스케일 Long-COT Instruction 데이터셋 기반 Slow-Thinking 모델 RedStar (Qwen-32B) 개발. 복잡한 문제 및 Multimodal Task에서 우수한 성능 입증 (MATH-Hard, AIME, GeoQA, MathVista-GEO 등).
- Multimodal Task 확장: Long-COT를 Multimodal LLM에 적용, Geometric Question Answering Task에서 성능 향상 확인. → Long-COT의 Textual 및 Multimodal Task 모두에서의 Versatility 입증.
결론 및 시사점:
- Long-COT 스케일링은 Reasoning 모델 발전에 변혁적인 잠재력 보유.
- 수학 문제 해결, Multimodal Task 등 다양한 영역에서 Long-COT Tuning 은 Reasoning 능력 향상의 핵심 도구.
- RedStar 모델은 Long-COT 방법론의 광범위한 영향력을 보여주는 선도적인 Reasoning 모델로 부상.
핵심 키워드: Long-COT, 데이터 스케일링, Slow-thinking reasoning, Sample efficiency, Model capacity, Reinforcement Learning, Multimodal, RedStar, Reasoning 성능 향상.
번역
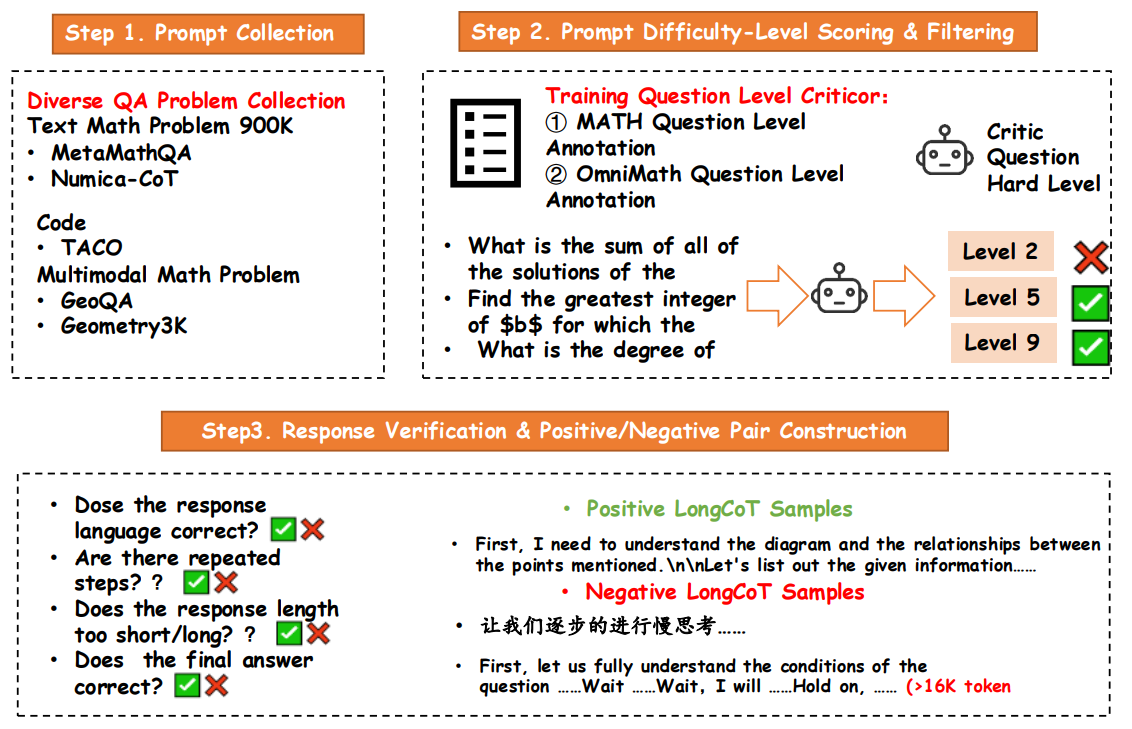
Figure 1: mathematics data의 Long-COT data curation 과정 개요.
과정은 세 단계로 구성됩니다:
(1) math, code-based, 및 multimodal datasets을 포함하여 다양한 sources로부터 prompts 수집;
(2) training을 위한 difficulty levels에 따라 prompts를 annotating 및 filtering; and
(3) response quality 평가 및 positive and negative samples 구성.
2 Long-COT Data Curation
Long chain-of-thought (Long-COT) reasoning tasks에서 models를 효과적으로 training하기 위해, 우리는 광범위한 mathematical problem-solving 시나리오를 포괄하는 high-quality dataset을 curated했습니다. 이 과정은 data crawling, augmentation, 및 rigorous verification을 포함하여 dataset이 scale에서 effective reasoning을 위한 specific requirements를 충족하는지 확인했습니다. 이 section에서는 Long-COT models training에 사용된 dataset을 assembling하고 refining하는 데 employed된 methodology를 자세히 설명하며, 이는 complex reasoning tasks에서 그러한 models의 performance를 enhancing하는 데 critical role을 합니다. 다음 content는 Metamath-qwen2-math dataset에서 derived된 long-COT training에 사용된 dataset의 curation 및 augmentation을 describes합니다.
Prompt Collection
Metamath-qwen2-math Overview: Metamath-qwen2-math dataset은 약 900k math problems을 contains하며, 각 problem은 chain-of-thought (CoT) solution을 포함합니다. 이는 MetaMathQA[8] 및 Numica-CoT[9]의 prompts를 utilizes하며, answers는 Qwen2-Math-72-instruct7에 의해 generated됩니다. 이러한 answers는 official solutions과의 alignment를 ensure하기 위해 rule-evaluation-toolkit8을 사용하여 rejection sampling을 undergo합니다. Dataset은 또한 aops_forum, amc_aime, 및 cn_k12와 같은 sources를 포함하여 NuminaMath-CoT의 diverse non-synthetic data를 incorporate합니다.
Code prompt collection을 위해 우리는 Codeforces, Leetcode, AtCoder 등에서 sourced된 25,443 training problems으로 구성된 TACO dataset의 problems를 utilize합니다. 각 problem은 algorithms, skills, 및 difficulty levels와 같은 fine-grained labels을 comes with합니다. Dataset은 또한 candidate code를 effectively evaluate하기 위한 test cases와 함께 diverse solutions를 provides합니다.
Multimodal tasks의 geometric scenes를 위해, 우리는 3,499 question prompts를 contains하는 GeoQA를 사용합니다. 각 prompt는 question과 closely related된 geometric textual information과 corresponding geometric image를 includes합니다.
Difficulty-Level Scoring and Augmentation
Qwen2.5-7B-Instruct를 사용하여 MATH 및 Omni-MATH datasets에서 trained된 difficulty-level model은 further augmentation을 위해 difficulty levels 7 이상인 problems를 selects합니다. 이러한 prompts는 QwQ model을 사용하여 multiple times sampled되며, higher difficulty levels에 대해 more samples가 generated됩니다. Answer correctness는 generated responses를 official answers와 comparing하여 validated됩니다.
Response Verification
Each question에 대해, 우리는 10 times sampling을 위해 QwQ로 보냈고 a large number of responses를 obtained했습니다. 우리는 overly repeated, non-target languages, 및 specified format으로 answers를 give하지 않은 Long-COTs를 remove하기 위해 manual rules를 사용했습니다. 이러한 positive samples는 SFT를 위한 Positive Samples로 retained되었고, verification을 pass하는 데 failed한 것들은 Negative Samples였으며, 이는 subsequent RL training에 used될 수 있습니다.
Code response collection을 위해, dataset의 each problem은 10 sampling attempts를 위해 QwQ에 given됩니다. Math-derived data와 유사하게, 우리는 first overly repeated data를 clean하고 incomplete code generation이 있는 Long-COTs를 remove합니다. 그런 다음, 우리는 TACO dataset의 test cases를 사용하여 QwQ에 의해 generated된 code를 test합니다. 우리는 all test cases를 pass하는 Long-COTs를 SFT를 위한 training data로 retain하며, ultimately 16,713 samples를 resulting합니다.
Final Dataset
Final dataset은 whole long-cot sft-datasets로서 difficulty levels 3-9인 220k prompts를 including하여 1000k samples로 consists됩니다. 우리는 또한 difficulty levels 7-9인 1.3k-prompts 및 4k correct prompt-response pairs를 including하는 subset을 derive합니다. Those high-quality datasets은 supervised fine-tuning (SFT)에 used되며 Qwen2-Math-7B 및 Qwen2.5-32B-Instruct9에서 trained된 models의 performance를 significantly improves합니다.
정리노트: Long-COT 데이터 큐레이션 (Section 2)
핵심 목표: High-quality Long-COT 데이터셋 구축을 통해 Reasoning Model의 성능 향상 (특히 수학 문제 해결).
큐레이션 프로세스 핵심 특징:
- 다양한 데이터 소스 활용:
- 수학 (Math): Metamath-qwen2-math (MetaMathQA, Numica-CoT 기반, Qwen2-Math-72-instruct 답변 생성, CoT 포함), NuminaMath-CoT (aops_forum, amc_aime 등 Non-synthetic data 포함) - CoT 솔루션이 이미 있는 대규모 수학 데이터셋 활용.
- 코드 (Code): TACO dataset (Codeforces, Leetcode 등, 알고리즘/기술/난이도 라벨, 다양한 솔루션, Test case 제공) - 코드 문제 해결 + 검증 가능한 Test case 활용.
- Multimodal (Geometric): GeoQA (Geometric Text + Image, 3499개 Question Prompt) - Multimodal Reasoning 평가를 위한 Geometric 데이터 포함.
- → 다양한 Domain (Math, Code, Multimodal) 및 데이터 유형 통합, General Reasoning 능력 학습 목표.
- 난이도 조절 및 데이터 증강 (Difficulty-Level Scoring & Augmentation):
- Difficulty Model 활용: Qwen2.5-7B-Instruct로 MATH/Omni-MATH 데이터셋 학습, 난이도 7 이상 문제 선별.
- QwQ 모델 활용 증강: 선별된 고난이도 Prompt를 QwQ 모델로 다회 Sampling, 고난이도 문제일수록 더 많은 Sample 생성 - 모델 능력을 넘어서는 어려운 문제에 집중, 효과적인 Curriculum Learning 유도.
- 정답 검증: 생성된 답변을 Official Answer와 비교하여 정확성 검증 - 고품질 Positive Sample 확보.
- Response 검증 및 Negative Sample 확보 (Response Verification):
- QwQ 10회 Sampling & Manual Rules 기반 필터링: 과도한 반복, 타겟 언어X, 지정 Format X Long-COT 제거 - 데이터 품질 확보 및 노이즈 제거.
- Positive/Negative Sample 분리: 검증 통과 Sample (Positive, SFT 사용), 실패 Sample (Negative, RL 사용 가능) - SFT + RL 활용을 위한 데이터 준비.
- Code Response Test Case 검증: TACO Dataset Test Case 활용, QwQ 생성 Code 검증, Test Case 통과 Code만 SFT 데이터로 활용 (16,713개) - Code 실행 가능성 기준 데이터 필터링, 높은 신뢰도 확보.
- 최종 데이터셋 구성 (Final Dataset):
- 총 1000k 샘플: Difficulty 3-9 전체 Long-COT SFT 데이터셋 (220k Prompts).
- 고품질 Sub-dataset: Difficulty 7-9, 1.3k Prompts, 4k Correct Prompt-Response Pairs - 고품질 데이터 집중, SFT 효과 극대화 목표.
- Qwen2-Math 모델 성능 향상 입증: Qwen2-Math-7B, Qwen2.5-32B-Instruct 모델 SFT에 활용, 성능 향상 확인 - 제안하는 데이터 큐레이션 방법의 효과 입증.
핵심 시사점:
- 난이도 조절 및 검증된 고품질 Long-COT 데이터셋 구축이 Scale Up 효과를 위한 핵심 요소.
- 다양한 Domain 데이터 통합 및 활용을 통해 General Reasoning 능력 향상 추구.
- Positive/Negative Sample 분리 및 RL 활용 가능성 제시.
- 실제 Code 실행 가능성 검증을 통한 Code Reasoning 데이터셋 신뢰도 향상.
연구 의의: 효과적인 Long-COT 데이터 큐레이션 방법론 제시, 고품질 데이터셋 구축 및 활용을 통해 Reasoning Model 성능 향상 가능성 입증.





